In acknowledging the myriad advantages of fiber optic broadband in enhancing career opportunities, telehealth, education, and public services accessibility, it’s essential to explore its environmental sustainability aspects. Let’s delve into the profound green benefits, both direct and indirect, that fiber optic broadband offers.
Energy Efficiency
Comparing energy consumption between fiber optics and traditional broadband reveals a staggering difference. Studies show that fiber-optic networks consume up to 70% less energy than conventional copper networks (Maverix) This efficiency stems from the superior data transmission capabilities of fiber optics, which generate minimal heat, thereby reducing the need for energy-intensive cooling systems in data centers and network infrastructures.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
Fiber optics, utilizing light signals instead of electrical currents, produce negligible electromagnetic fields and emit minimal carbon dioxide during data transmission. Embracing fiber optic broadband for remote work not only enhances personal convenience but also contributes significantly to reducing carbon emissions associated with commuting. By enabling a commute-free workday, fiber optic broadband helps mitigate transportation-related carbon footprints, thereby promoting cleaner air quality. This aligns with global efforts to mitigate climate change and achieve sustainable development goals (UNEP, 2020).
Ecosystem and Resource Friendly
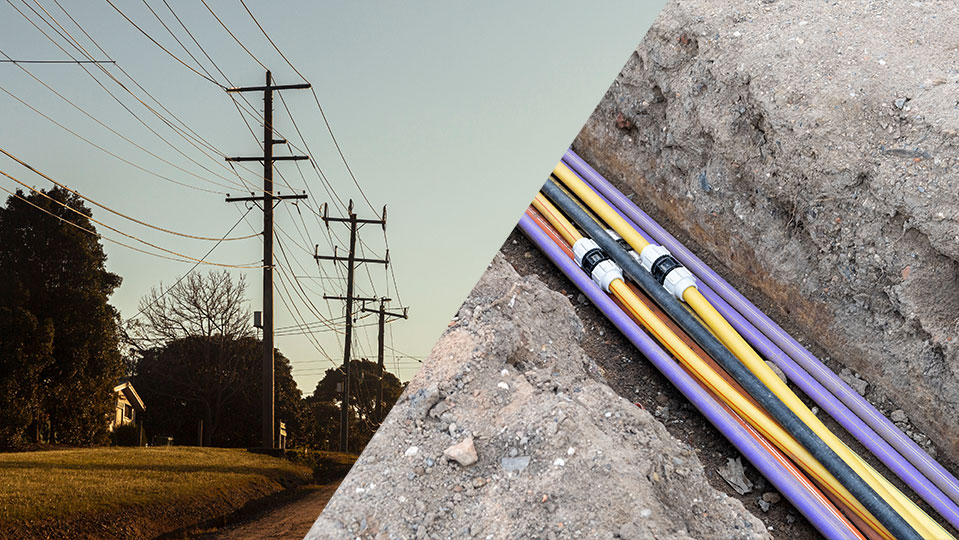
The utilization of fiber optics contributes to environmental conservation by minimizing deforestation, habitat destruction, and resource depletion. Unlike copper cables, which rely on non-renewable materials and entail environmentally impactful mining processes, fiber-optic cables are primarily composed of silicon dioxide, an abundant and easily accessible raw material with minimal environmental impact during extraction. Additionally, the longer lifespan of fiber-optic cables translates to reduced resource consumption and waste generation compared to copper cables, further contributing to climate change mitigation efforts (IPCC, 2019).
Societal and Economic Benefits
Fiber optic broadband plays a pivotal role in empowering underserved communities through sustainable infrastructure. Its durability, high-speed connectivity, and reliability facilitate competitive work, educational opportunities, telehealth access, and public service delivery irrespective of geographical constraints. The seamless connectivity and productivity enhancements offered by fiber optic broadband, particularly in remote work settings, underscore its societal and economic significance in fostering resilient communities and economies resilient to climate change impacts (World Bank, 2021).
Working from home is less problematic and more productive with reliable, durable fiber. It offers lightning-fast speeds for quick processing and reliable web connectivity, less connection disruptions and more security than other broadband forms, uniform upload and download speeds that eliminate lag time even with multiple devices in use, and it is an adaptable, scalable form of technology that can accommodate future innovations.
A Greener Future through Policymaking
A proactive approach to promoting green technology, coupled with supportive government initiatives, can accelerate the adoption of fiber optic broadband. Regulatory frameworks incentivizing fiber optic deployment, especially fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) initiatives, hold the potential to drive significant investments in sustainable broadband infrastructure. By aligning with national climate goals and fostering technological advancements, fiber optic broadband emerges as a cornerstone in the global efforts to combat climate change and build climate-resilient societies (OECD, 2022).
As we navigate towards a sustainable future, fiber optic broadband stands out as a catalyst for environmental preservation, economic growth, and societal progress. By harnessing its green benefits and leveraging policy interventions, we can pave the way for a greener, more connected world powered by resilient and sustainable broadband infrastructure, contributing to global climate change mitigation efforts and sustainable development objectives.
Northwest Open Access Network (NoaNet) is a not-for-profit wholesale telecommunications mutual corporation that has been serving Washington State since 2000. As a mission-driven organization, NoaNet focuses on bringing world-class telecommunications technology to hard-to-reach communities which lack access to high-speed affordable broadband services.
Sources and recommended reading: United Nations Environment Programme, Lumos Fiber, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Frontier, The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, LinkedIn Telecommunications Community, Maverix Broadband, Ting Internet, and Chariton Valley.